Location
The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan is strategically located in the Middle East. Bound by Syria to the north, Iraq to the northeast, Saudi Arabia to the east and south, the Red Sea to the south, and Israel and the Palestinian National Authority to the west, Jordan covers a diversity of landscapes. The country has an area of 89,213 square kilometers, with approximately 75% of that space being taken up by desert.
Jordan is a land steeped in history. It has been home to some of mankind’s earliest settlements and villages, and relics of many of the world’s great civilizations can still be seen today.
Geographically, Jordan enjoys a range of geographical features, starting from the Jordan Rift Valley in the West ending at the desert plateau of the East, with a range of small hills running the length of the country in between.
The climate in Jordan is characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters, with annual average temperatures ranging from 12 to 25 C and summertime highs reaching the 40 C in the desert regions. Rainfall averages vary from 50 mm annually in the desert to 800 mm in the northern hills, some of which falls as snow.
Politics
The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan is a constitutional monarchy with representative government, based on a Constitution established in 1952. The reigning monarch, His Majesty King Abdullah II is the head of state, the chief executive and the commander-in-chief of the Jordanian armed forces. The King exercises his executive authority through the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers, or Cabinet.
The Cabinet, meanwhile, is responsible before the elected House of Deputies which, along with the House of Notables (Senate), constitutes the legislative branch of the Government. The judicial branch in Jordan is an independent branch of the Government.
While the Kingdom itself may be young, the people who inhabit it have, like their ruling family, an immensely long and distinguished past. The land that is now Jordan lies in a position of strategic and geographic importance, a crossroads where the Spice and Silk Routes from eastern Asia to the Mediterranean met the north-south axis of the trade routes from Turkey and Syria down to Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
Jordan has a reputation for dynamism, moderation and peace brokering in the Middle East. His Majesty King Abdullah II rules over a state, which has peacefully absorbed Palestinian refugees over the past thirty years. Jordan with a majority Islamic population and a Christian minority remains an oasis of peace in a troubled region.
Climate
Jordan’s climate is arid, and moderate in temperature. Winter temperatures in Amman average around 7 – 10 C in January, with July temperatures reaching 23 – 27 C. Average annual rainfall varies from less than 50 mm to over 600 mm in certain parts of the country. Amman, at over 950 meters elevation, is known for its cool, dry nights even in full summer.
Population
Jordan’s population is about 5 million. Gender distribution is fairly even at 52% male, 48% female, The country is young, with 40% of the population under the age of 15, and only 3% over the age of 65.
Islam is the predominant religion. 92% of the people are Sunni Muslims. 6% are Christians, while the remainder are Shia Muslims, Sunni Circassians, Chechens, Druze, and Bahai. The Muslim New Year and other Islamic holy days are public holidays.
Language
Arabic is the official language, but English is spoken widely, especially in business.
Currency
The unit of currency is the Jordanian Dinar, and the rate of exchange is 1.42 USD
Time Zone
Time is GMT (+ 2 in winter, + 3 in summer), or 7 hours ahead of US Eastern Standard Time. Summer time is observed from April through September.
Working Days and Hours
Most private businesses observe Friday as the weekly holiday, while banks and government offices close on Fridays and Saturdays. Jordanian labor law limits most workers to 48 hours per week, the exception being hotels, restaurants and cinema workers with 54 hours. Annual paid leave is 14 days, 21 days for workers over five years with the same employer.
Visas
Visas are required for entry into Jordan. Fees and length of stay vary according to the visitor’s nationality. Visas can be obtained from either a Jordanian diplomatic mission, or for some nationalities, at point of entry.
Standard of Living
Jordanians enjoys a higher standard of living in general, where consumers have a wide range of modern goods and services at affordable prices. The social life, it is rich and varied, especially in the center of the capital, Amman. The people of Amman are famous worldwide with hospitality and kindness as investors and pioneers and foreign staff and visitors coming to Jordan finds that the social and intellectual life, business and projects in Amman hospitable and attractive and varied.
Education
Education in Jordan has the highest priority, so the country hold the lowest percentage of illiteracy in the Middle East and North Africa, the proportion of education in Jordan has reached in 1996 (88.2%). In Jordan Twenty-two University provides opportunities for students to obtain advanced degrees in the arts and sciences, which created a large number of university and college graduates in the labor market. The total number of students enrolled in schools 115,842 students and seeks about another 20 thousand Jordanian to obtain advanced degrees from abroad.
Schools in Jordan offers foreign expatriates who wish to live in Jordan, an education of high level in Arabic, English and French. Also a large number of foreign schools – which internationally recognized, provide courses to complete the Jordan’s high school diploma requirements.
As for working mothers they could easily access preschool and day care centers, registration fees in preschool and day care centers ranging from $70 to $150 per month.
Transportation

Arriving visitors to Jordan land at the Queen Alia International Airport, which is comfortable and modern. Where the airport is located 30 kilometers south of Amman, which is linked with 26 international airlines. The Royal Air carrier (Royal Jordanian Airlines), they are running regular flights to 47 major city around the world.
In Jordan, an extensive network of paved roads that allow comfortable movement of vehicles without delay to all regions in the country. Thus, providing personal transportation is easy, as there are in Jordan more than 100 Metro Agency offers a variety of rental vehicles for the purpose of short and long-term, as well as the yellow taxi cars always present efficiently and provide services at very reasonable prices. The expatriates who want to drive a car in Jordan, they could use the international driving licenses legally during short-term stays. But for residency for a long time, having a Jordanian license is necessary and possible by displaying foreign valid driving license.
Health Care
The level of health care in Jordan are among the best in the region. Jordan is the first country in the region that has embraced heart transplant. The average number of doctors available in Jordan 19.8 per 10,000 inhabitants where Jordan exceed this figure many developed countries (the United Kingdom, for example, 15.1). The health services in Jordan built on international standards and there is a growing number of private hospitals and clinics, which includes ultra-modern facilities and equipment operated by skilled local and international personnel. There are currently (50) private hospital in Jordan contains a total of a beds (3168) beds, also other hospitals aare being licensed and the established. Where the proportion of the number of beds in hospitals in the public and private sectors per 10,000 inhabitants (18) beds.
Economy
Led by an active private sector, Jordan’s economy is free market oriented. The ownership of enterprises is largely private, the exception being public sector involvement in the mining industry. Prices (except for a few subsidized goods) interest rate, and wages are generally determined by market forces.
During the last decade, Jordan’s economy has been making steady progress through the implementation of comprehensive economic reforms and restructuring programs supervised by the IMF and the World Bank.
Jordan’s economy is heading mainly toward services. This sector provides financial and business services, transport and communications, tourism, construction and education. And contributes 71% of GDP and employs two-thirds of the workforce. The remainder, amounting to 29% thus contributing by industry, agriculture and mining sectors.
Tourism
In addition to the country’s political stability, the geography offered makes Jordan an attractive tourism destination. Tourism is of vital importance to the national economy of Jordan. It is the Kingdom’s largest export sector, its second largest private sector employer, and it’s second highest producer of foreign exchange. Tourism contributes more than US$800 million to Jordan “s economy and accounts for approximately 10 percent of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP).
Jordan’s major tourist activities include numerous ancient places including Petra, its unique desert castles and unspoiled natural locations to its cultural and religious sites.
Jordan is home to the Dead Sea, which is considered the lowest point on earth lying – 408 meters below the Sea Level. The highest point in Jordan, in contrast, is Jebel Umm El Dami, which lies 1854 meters above sea level.
Some of Jordan’s historical treasures and many major attractions are distributed in all the cities, which are:
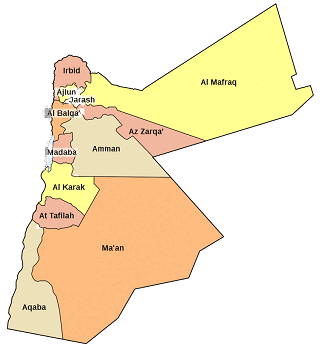
- Amman
- Azraq
- Jordan Valley & The Dead Sea
- Karak
- Petra
- Wadi Rum
- Aqaba
- Jerash
- Ajloun
- Irbid
- Salt & Fuheis
- Madaba

